Digestive System Tour Lab Teacher Guide
Welcome to Ms. Stephens’ Anatomy & Physiology Class Email: Class website: Tutorial: 3:45-4:45 Wednesdays, or schedule an appointment. Announcements: The class website contains lesson plans, notes, and study links. Please check the lesson plans to see what you missed, and for make-up work. Notice to Parents & Students: The class website is regularly updated for each unit. Students are expected to check the class website prior to the next class when they are absent to not get behind. There are many study resources available as well!
Course Syllabus : -19 . Please download the Course Syllabus by clicking the link above and confirm you have read the course syllabus by clicking the link below and completing the following form. . Unit 4: Skeletal System 1. Identify and describe the functions of the skeletal system. 2.Distinguish between long bones, short bones, flat bones, and irregular bones and provide an example of each.
3.Identify the parts of a typical long bone. 4.Describe the microscopic structure of compact bone, and compare it with that of spongy bone. 5.Explain the process by which bones are formed and how they growth in length and width. Diagnose specific types of bone fractures on X-ray images. 7.Describe and diagnose disorders of the skeletal system Essential Questions:. How is the structure of bone related to its function?.
What changes occur in bones as you age?. How does the skeletal system help the body maintain homeostasis?. What are the strengths and limitations of the body's joints? Skeletal System Classwork: Coloring: Labeling: Case study-Fractured leg Videos: Practice Quizzes: (picture) (matching).
Unit 5: Muscular System Student Learning Goals:. I can identify smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissue under a microscope and state the function of each. I can identify the component parts of a muscle: fascicle, myofibril, fiber, nucleus of cell, body of muscle.
I can identify the major muscles of the human body. I can analyze experimental data using the Moving Arm Model and interpret the meaning of the data.
Unit 5:. Unit 5: Muscle Pointing Review PPT.
Video:. Unit 5: Muscular System Chapter of Anatomy Textbook. Unit 5:. Unit 5:. Unit 5:. Unit 5: Web Resources for the Muscular System Unit Link: Classwork: -you are a personal trainer.
Cat Dissection Learning Objectives: 1. SWBAT identify and describe the principal structures of the cat brain; IOT relate each to its function in the body. SWBAT identify important parts of the cat brain in a preserved specimen; IOT demonstrate techniques used by scientist in the lab. read about the history of autopsies - Lists all of the structures you will need to identify on the cat - answer as your group dissects the cat, describe the anatomy, structures and locations - shows the main structures you will need to identify for the cat practice.
The Ultimate Fetal Pig Dissection ReviewUse the following resources to review the anatomy of the pig. Be sure to look through all of your lab handouts and be able to label the all of the pig images. The Dissection Virtual Pig Dissection Fetal Pig Photos Drawings of PigsWhile pictures are useful for learning the anatomy of the fetal pig, be careful with only memorizing drawings.
Real pigs are not as cleanly pictured and the parts not perfectly aligned. Be sure to study the real pig photographs also. Fetal Pig Practice Quizzes- fill in blanks and self check. If you want an authentic experience, print out the. this set has flashcards and a practice quiz showing the internal and external anatomy.
Unit 6: The Nervous System Learning Objectives:. Describe the function and main structures of the nervous system. Describe the state of a resting neuron, including the charges inside and outside the cell. Explain how an impulse is sent through a neuron, including what an action potential is. Explain how an impulse is sent from one neuron to the next at the synapse, including the role of neurotransmitters. Compare and contrast the CNS and PNS in terms of their structures and functions. Describe the four lobes of the brain and what types of activities each controls.
Compare and contrast the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic NS. Explain the importance of a reflex and how reflexes can occurs so quickly. Unit 7: Sensory Systems Learning Goals:. Describe the 5 types of sensory receptors and where they are found.
Describe the two chemical senses. Explain how we hear. Explain how we see. Midterm Project Web Resources: 'Measuring your taste threshold' 'Now you see it now you don't'When your sniffer snoozes you've got olfactory fatigue'Do video game players have faster reaction times than non players?' Circulatory System Learning Goals: .
SWBAT analyze the physical, chemical, and biological properties of process systems as these relate to transportation, absorption and excretion, including the cardiovascular systems.SWBAT Analyze, and explain the relationships between the respiratory and cardiovascular systems as they obtain oxygen needed for the oxidation of nutrients and removal of carbon dioxide.SWBAT Relate the role of the urinary system to regulation of body wastes (i.e. Water electrolyte balance, volume of body fluids). Digestive System/Excretory System Learning Goals: 1. Describe the functions of the digestive system. Compare and contrast chemical and mechanical digestion.
Describe the pathway of food through the alimentary canal organs (7 total) and for each organ, state the type of digestion (mechanical and/or chemical) that occurs. If chemical digestion occurs, additionally state what enzyme is involved and what is broken down.
Explain the role of the pancreas and describe each of the five pancreatic secretions. Flight: Social and Economic issues will also be discussed as it relates to human reproduction and human populations. Re productive System Learning Goals:.Students will analyze the role of the reproductive system as it pertains to the growth and development of humans. Explain how the functions of the reproductive organs are regulated by hormonal interactions. Describe the stages of human embryology and gestation including investigation of gestational and congenital disorders (e.g. Ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, cleft palate, hydrocephaly, fetal alcohol syndrome). Describe the stages of development from birth to adulthood (i.e.
Neonatal period, infancy, childhood, adolescence and puberty, and maturity).
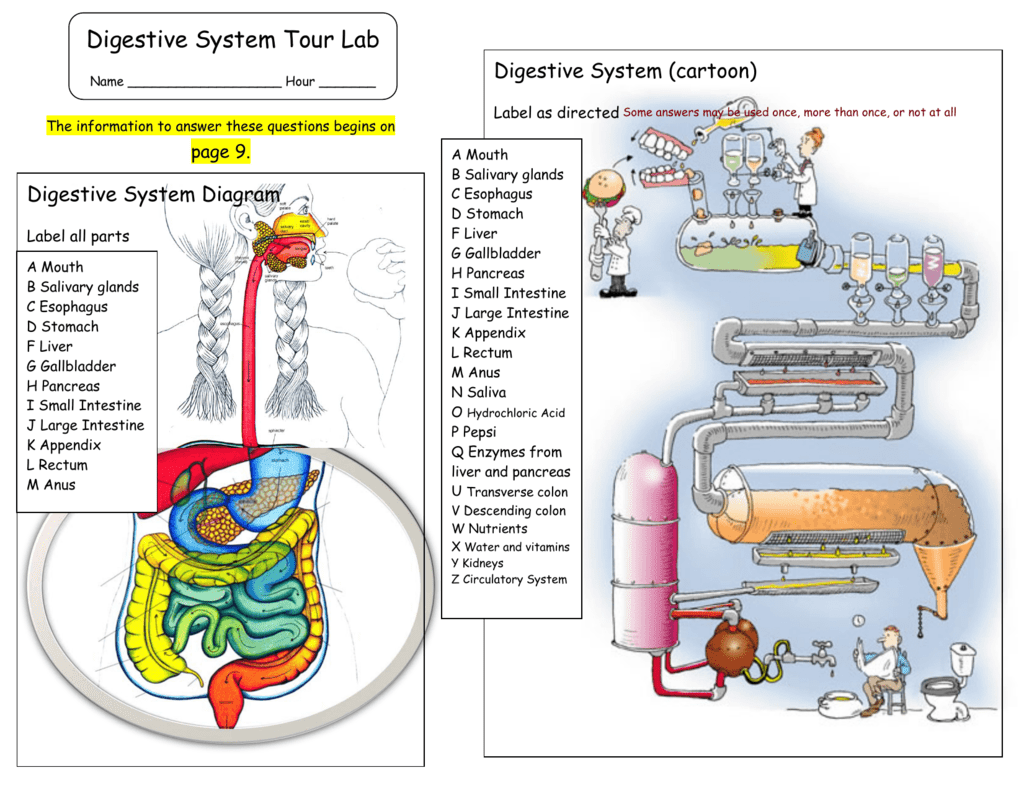
1 Digestive System Tour Lab Name Hour The information to answer these questions begins on Digestive System Diagram Label all parts A Mouth B Salivary glands C Esophagus D Stomach F Liver G Gallbladder H Pancreas I Small Intestine J K Appendix L Rectum M Anus page 9. Digestive System (cartoon) Label as directed A Mouth B Salivary glands C Esophagus D Stomach F Liver G Gallbladder H Pancreas I Small Intestine J K Appendix L Rectum M Anus N Saliva O Hydrochloric Acid P Pepsi Q Enzymes from liver and pancreas U Transverse colon V Descending colon W Nutrients X Water and vitamins Y Kidneys Z Circulatory System 2 Digestive System Tour Lab Page 2 A.D.A.M. Video clip: Digestion Fill in the blanks Food is digested by the churning of the stomach walls and by secretion of. (chemicals) speed up the breakdown of food. Trypsin breads down found in.
Lipase breaks down the found in and butter. Breaks down the sugar in milk. Food is moved through the small intestine where are absorbed and enter the. Blood is taken to the liver where are processed and are removed.
The absorbs water and compacts the remainder of the feces. Feces are eliminated through the. Video clip: Peristalsis A.D.A.M.
Video clip: Heartburn Fill in the blanks Heartburn does not involve the heart, but is felt in the near the heart s location. The has a protective lining against the acid, but the does not. Relieve heartburn by making the stomach juices less acidic. Video clip: Swallowing Fill in the blanks Stage 1 pushes food into the throat. Stage 2 folds over voice box at entrance of windpipe. Stage 3 in the esophagus contract.
Fill in the blanks Peristalsis is a series of contractions that moves food through the digestive tract. Mixes and shifts the chime on the intestinal wall. Video clip: Ulcers Fill in the blanks The stomach produces that breaks down food into simpler substances. The lining keeps the stomach from digesting itself. If the lining becomes too thin, an may form. Ulcers may be caused by bacteria, not stress.
To control the bacteria, are prescribed. The Esophagus Connects the. Made of several layers of. Is the wavelike muscle contractions that force food through the digestive tract. 3 Digestive System Tour Lab Page 3 The Digestive System is a Giant Food Processor Match These: breaking down of food by the action of enzymes stored for future use The Mouth Food is.
Saliva moistens. Broken down into glucose building blocks of cells broken down into amino acids used by cells for energy bile and enzymes from liver enter here water goes back into the bloodstream proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals go into blood (A) small intestine (B) duodenum (C) carbohydrates (D) chemical digestion (E) fats (F) amino acids (G) proteins (H) glucose (I) large intestine The tongue moves. The Throat: The epiglottis. The Salivary Glands: Produce. Saliva is an enzyme that. Food becomes moist and mushy. It is now called a.
The Stomach (match these): Nutrients the stomach s own acid begins to eat through the stomach Nutrients are absorbed through the. Control the ends of the stomach food enters the stomach through the digests protein and kills bacteria helps the hydrochloric acid digest proteins.
3 strong layers of muscle (A) Mucus (B) Hydrochloric Acid (C) The stomach (D) Sphincter muscles (E) Esophagus (F) Ulcer (G) Pepsin Describe the inside lining of the small intestine. Draw a diagram of the villi and label its parts. Villi 4 Digestive System Tour Lab Page 4 Your Teeth are Specialized An adult has teeth. Incisors are for. Canines are for.
Premolars and molars are for. Another name for the 3 rd molars is the teeth. Label the teeth in the diagram: A F Tooth Anatomy Hardest part of the tooth is the lies just beneath the enamel.
Is a soft tissue that contains living nerve cells. B C D G H H G F E D C B A E Small Intestine The longest.
Divided into 3 parts: first segment second segment third segment Digestive enzymes. To stomach Label the Small Intestine: duodenum jejunum illium 5 Digestive System Tour Lab Page 5 In the large intestine, and are absorbed back into the blood to be reused. What does the appendix do? Label the: ascending colon transverse colon descending colon appendix rectum anus Tommy Torso (match Tommy s parts with their number) Check Out this X-ray Part name Tongue Part number Return all of my parts before leaving The digestive system organ colored yellow is probably the. Salivary Gland this station!!!!! Esophagus The digestive system organ colored pink is probably the. Stomach Liver What is the doctor about to tell Kermit?
Gallbladder Pancreas Duodenum Small Intestine Which Digestive System organ is shown in this x-ray? Appendix What name does Tommy prefer?
15 View the Video clip from A.D.A.M. Found on the Human Biology/Links page of our website ( Digestion Answer all questions on the answer sheet Click here 16 View the Video clip from A.D.A.M. Found on the Human Biology/Links page of our website ( Heartburn Answer all questions on the answer sheet Click here 17 View the Video clip from A.D.A.M. Found on the Human Biology/Links page of our website ( Peristalsis Answer all questions on the answer sheet Click here 18 View the Video clip from A.D.A.M. Found on the Human Biology/Links page of our website ( Swallowing Answer all questions on the answer sheet Click here. 19 View the Video clip from A.D.A.M. Found on the Human Biology/Links page of our website ( Ulcers Answer all questions on the answer sheet Click here 20 The Digestive System is a Giant Food Processor Mechanical Digestion Food is chopped and ground into small pieces in the mouth.
Chemical Digestion Food is broken down into simple nutrients by the chemical action of enzymes. Nutrients Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars (glucose) which is used by the cells for energy.
Proteins are broken down into amino acids (the building blocks of cells) which are used to repair old cells and build new cells (skin, blood, muscle, bone and nerve). Fats are stored for future use. They contain vitamins.
21 The Mouth Food is cooled or warmed to body temperature. Teeth chop and grind food and the tongue mashes the food. Saliva moistens the food and begins breaking down carbohydrates. The tongue moves the food to the back of the mouth to be swallowed. The Throat The Epiglottis closes off the wind pipe (trachea). Muscles push food into the esophagus.
The Salivary Glands Produce saliva. Saliva is an enzyme (chemical) that begins the breakdown of starches. Food becomes moist and mushy so that it can be easily swallowed. The food is now called a Bolis. 22 3rd Molar (wisdom tooth) 2 nd Molar 1 st Molar Incisors Premolars Canine (Wisdom teeth) Your Teeth are specialized An adult has 32 teeth including 4 wisdom teeth. The Incisors are shaped like knives for cutting and slicing.
The Canines have points for piercing and tearing. The Premolars and Molars have broad, bumpy surfaces for grinding. Tooth Anatomy Enamel is the hardest part of tooth.
Made mostly of mineral. Dentin is softer than enamel. Contains some living cells. Pulp is also called the nerve of the cell.
It is a soft tissue that contains living nerve cells. 23 The Esophagus Connects the pharynx (throat) to the stomach. About 10 inches long. Flat when empty but changes shape to allow food to travel to the stomach.
Made of several layers of muscle that push food through to the stomach (peristalsis). Peristalsis is the name given for the wavelike muscle contractions found in the esophagus, small intestines and large intestines. It is sort of like squeezing toothpaste through a tube. Bottom s up I mean down I mean. Peristalsis Esophagus Yes, it is even possible to drink while upside down!!
24 The Stomach Food enters the stomach from the esophagus. Hydrochloric Acid is produced in the stomach to digest proteins and kill off bacteria. Pepsin (a digestive enzyme) is produced to help digest proteins. Mucus is produced by glands of the stomach to protect the stomach from its own acid.
Sphincter muscles control both ends of the stomach to allow food to enter and exit. The stomach is made of 3 strong layers of muscle which mixes and mashes the food with digestive enzymes. An ulcer forms when the stomach s protection breaks down its own acid begin to eat through the stomach. Stomach Stomach 25 Small Intestine Small Intestine The longest part of the alimentary canal (digestive tract). Divided into 3 parts: Duodenum first segment Jejunum middle segment Illeum last segment Digestive enzymes from the liver and pancreas help to break down food further. Nutrients are absorbed into the body through the villi.
Duodenum Jejunum Illeum 26 The Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas The Liver produces the enzyme (chemical) bile Bile breaks down fats. Bile is stored in the gallbladder and enters the duodenum (1 st part of small intestine) when needed. The Pancreas produces ½ to 1 liter of enzymes (chemicals) daily.
These enzymes are used to break down carbohydrates as well as fats and proteins. Liver Pancreas The Liver: Stores vitamins Stores glycogen for energy Breaks down old red blood cells Removes poisons from the body Enzymes from the liver and pancreas enter the small intestine at the duodenum Liver Pancreas Gallbladder 27 Nutrients are absorbed through the small intestine where the blood carries them to all the cells of the body.
The Basic Nutrients are: Amino Acids Simple Sugars Fatty Acids Small Intestine The inside lining of the small intestine contains Villi. These Villi tiny are fingerlike projections through which the nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream. The Villi capture nutrients as they move through the small intestine.
Villi Blood vessels Photograph of Villi magnified (very high power) Note; your microscope will not show nearly the detail as in this picture. Glands secreting digestive enzymes 28 In the: Indigestible parts of food move from the small intestine to the large intestine. Water and vitamins are absorbed back in the blood to be reused. The remaining waste passes to the RECTUM where peristalsis forces it through the ANUS and out of the body.
Large intestine Rectum The is made of 3 parts: Ascending colon Transverse colon Descending colon Note: The Appendix serves no useful purpose. Perhaps it had a role in digesting rough foods many, many years ago. (transverse colon) (ascending colon) (descending colon) Appendix Anus Rectum 29 Try to swallow this some interesting facts about your digestive system. The average digestive tract (alimentary canal) is 27 feet long!
During a lifetime, a person will process between 60,000 to 100,000 pounds of food! Just the sight and smell of food begins the digestive process (saliva in your mouth, esophagus begins to ripple, stomach produces digestive enzymes) Your stomach can expand to hold 2 ½ pints of food. The liver is the body s second largest organ weighing 3-4 pounds. (the skin is the largest organ) A meal takes between 15 to 48 hours to completely digest and move through the alimentary canal.
30 Which Digestive System organ is shown in the x-ray? Hint: It stores Bile that was produced in the liver. (If this doesn t help, do some other stations first) 31 Check out this x-ray: The digestive organ colored yellow is probably the Small intestine Large intestine Heart Pancreas The digestive organ colored pink is probable the Small intestine Large intestine Heart Pancreas (answer on your lab answer sheet) Hint: if you are not sure, do some other stations first.
Have a seat, Kermit. What I m about to tell you might come as a big shock. 32 This is Tommy the Torso (but he prefers Elvis). Tommy is an expensive, hand painted model of the human torso. His organs are removable but must be handled with care.
Carefully remove the Liver, Stomach, and Intestines. Locate and identify the following parts and match them with the numbers on the model: Tongue Salivary Gland Esophagus Stomach Liver Gallbladder Pancreas Duodenum Small Intestine Appendix Rectum Choose from these numbers: 111/ /124 Return all parts before leaving this station. Ask if you need help /138/139 Place all answers on you lab answer sheet 33 Your Saliva contains the enzyme amylase which breaks down huge starch molecules into smaller simple sugars. A cracker is mostly carbohydrate (starch) but if you leave it in your mouth long enough, it will become sugar and you will notice a sweet taste!! Take one unsalted cracker and chew but don t swallow. Keep the bolus (chewed mush cracker) in your mouth for a minute. After you notice the sweet taste you may swallow.
Digestive System Lab Test
Only one quacker per customer!! Crackers are located on the front lab table.
34 How many Digestive System pig parts can you find in this Fetal Pig Model? 38 Build a paper model of the digestive system that looks like the picture below!! Color each part so that it looks very similar to the picture. Cut out each part carefully and tape it to the outline.
Parts must be taped down in the proper order beginning with the pancreas. Cut out the outline with all of the parts. Find the place on your lab answer sheet labeled Tape Paper Digestive System Here and tape your completed paper digestive system in that place. Liver Stomach Gallbladder Small Intestine (duodenum) (Transverse Colon) Pancreas Small Intestine (Illium) (Ascending Colon) Appendix Rectum Anus (descending Colon) Small Intestine (Jejunum) 39 On the computer Go to the Human Biology/Links page of our science website ( Click on Digestive System Tour Lab Find this page in the lab and click on the links. Answer all questions on your lab answer sheet: 1.
Digestive System Lab Activity
A Balanced Diet Also found at Human Biology/Links page 2. Malnutrition Also found at Human Biology/Links page 40 Write these steps of digestion in their proper order. They are all messed up here. Summary of Digestion Hydrochloric acid and pepsin digest proteins in the stomach. The stomach squeezes to mix food. Nutrients are absorbed into the blood by villi in the small intestine.
Water is absorbed from the food waste back into the body. The tongue pushes food to the back of the mouth where it is swallowed. Food is chopped and ground in the mouth. Bile (produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder) enters the small intestine to break down fats. Solid waste material is forced out of the body by action of both voluntary and involuntary muscles (if ya know what I mean). Food moves to the small intestine (through the duodenum). Waste (food) leaves the small intestine and enters the large intestine.
The food moves along the esophagus to the stomach.